Diagnosing post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD) is challenging and often requires invasive procedures. Analyses of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) isolated from plasma is minimally invasive and highly effective for genomic profiling of tumors. We studied the feasibility of using cfDNA to profile PTLD and explore its potential to serve as a screening tool. We included seventeen patients with monomorphic PTLD after solid organ transplantation in this multi-center observational cohort study. We used low-coverage whole genome sequencing (lcWGS) to detect copy number variations (CNVs) and targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) to identify Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA load and somatic single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in cfDNA from plasma. Seven out of seventeen (41%) patients had EBV-positive tumors, and 13/17 (76%) had stage IV disease. Nine out of seventeen (56%) patients showed CNVs in cfDNA, with more CNVs in EBV-negative cases. Recurrent gains were detected for 3q, 11q, and 18q. Recurrent losses were observed at 6q. The fraction of EBV reads in cfDNA from EBV-positive patients was 3-log higher compared to controls and EBV-negative patients. 289 SNVs were identified, with a median of 19 per sample. SNV burden correlated significantly with lactate dehydrogenase levels. Similar SNV burdens were observed in EBV-negative and EBV-positive PTLD. The most commonly mutated genes were TP53 and KMT2D (41%), followed by SPEN, TET2 (35%), and ARID1A, IGLL5, and PIM1 (29%), indicating DNA damage response, epigenetic regulation, and B-cell signaling/NFkB pathways as drivers of PTLD. Overall, CNVs were more prevalent in EBV-negative lymphoma, while no difference was observed in the number of SNVs. Our data indicated the potential of analyzing cfDNA as a tool for PTLD screening and response monitoring.
Windows en Linux
Houdt de toets ctrl ingedrukt en draai het muiswiel omhoog of omlaag
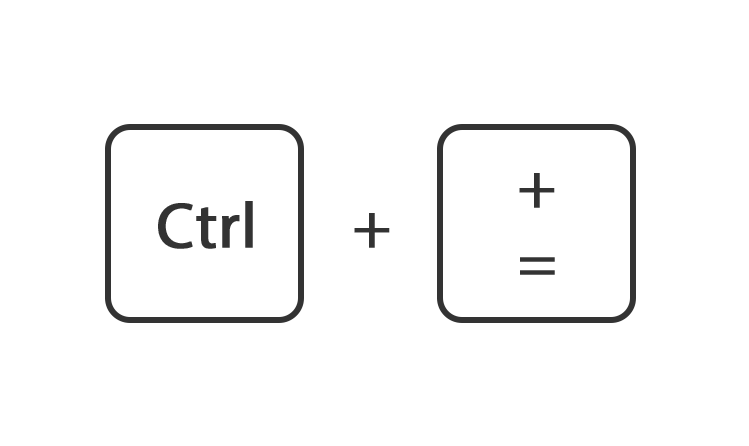
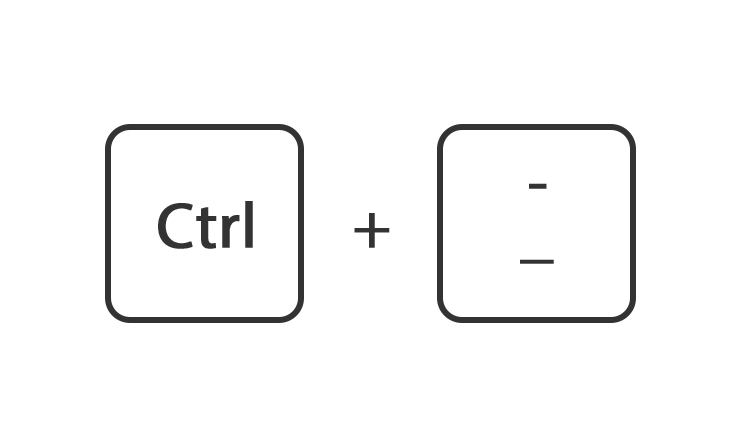
Of houdt de toets ctrl ingedrukt en druk tegelijk op de toets + of -
Of ga rechtsboven naar instellingen en gebruik de instelling zoom
Mac
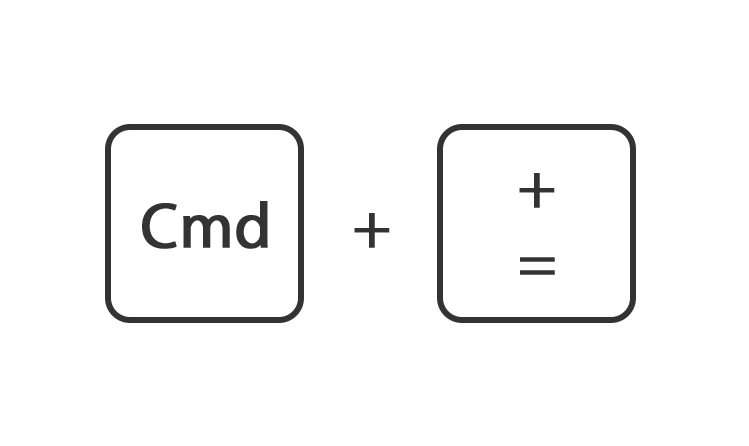
Houdt de toets command ingedrukt en druk op de toets + of -
Of ga rechtsboven naar instellingen en gebruik de instelling zoom.